A Serverless Distributed Ledger for Enterprises
In January I will be presenting at the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS – 55). I’m happy to have our publication selected – and it was great to see a record-breaking volume of submissions this year! After the event, HICSS participants can download conference papers and view video presentations on-demand. Until then, this post summarizes our presentation and provides a link to our original research.
Before learning more about the paper and our research, it might be helpful to discuss why we engaged in it in the first place … startups are laser-focused on outcomes, so why stop to write research papers? Our answer is two-fold: First, we believe that being customer-obsessed requires learning from many customers and creating products that reflect that learning. Sharing the results of our studies on the requirements for blockchains in the enterprise helped us, and now hopefully will help others, create better, more customer-centric products and services. Secondly, we’re breaking new ground, and we want to share that story. Building a consensus and data replication system in the cloud that simultaneously achieves low latency, high scale, tight cost enveloping, zero infrastructure footprint, and ACID semantics isn’t easy … and having a peer-reviewed conference article helps establish that Vendia is doing ground-breaking work that sits at the intersection of blockchains, conventional databases, and cloud-native design. We hope you find these topics as intriguing as we did!
Research Summary
Enterprises have been attracted by the capability of blockchains to provide a single source of truth for workloads that span companies, geographies, and clouds while retaining the independence of each party’s IT operations. However, so far production applications have remained rare, stymied by technical limitations of existing blockchain technologies and challenges with their integration into enterprises’ IT systems.
In our paper, we collect enterprise requirements for blockchains or ledger-like offerings to enable cross-organization data exchange and propose an approach that combines many of the decentralization benefits of conventional distributed ledger approaches with the advantages of multi-tenanted, centralized cloud services.
Serverless Overcomes Common Distributed Ledger Challenges
We found that many of the limitations organizations face regarding performance, complexity, and cost in existing enterprise distributed ledger implementations are driven by their reliance on a server-based deployment model. We suggest an intriguing alternative: a distributed ledger in which each node is built using “serverless” infrastructure, thus benefiting from the economic and scaling advantages of massive multi-tenanted implementations that expose inter-machine parallelism opportunities unavailable to prior techniques. At the same time, this approach also dramatically reduces deployment, scaling, and fault tolerance complexity for the owners and maintainers of those deployments.
Achieving a Single Source of Truth
While blockchains may be employed for a wide variety of purposes, our approach aligns with the needs of business users attempting to construct a “single source of truth” among mutually distrustful business parties. Our contributions include exploration of blended approaches that lie neither in centralized nor in conventional (“server-based”) decentralized algorithms. Our approach is capable of exploiting massive multi-machine parallelism to overcome scaling and smart contract processing limitations inherent in the conventional “single-box” blockchain implementations used by Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, Quorum, and others, while still exhibiting useful decentralized outcomes such as operational and ownership isolation and consistent data replication among nodes.
Key Requirements & Capabilities
Our research includes qualitative and quantitative approaches. We discuss our approach to implementing a permissioned blockchain from a qualitative perspective, structured according to the business requirements we collected from 1,092 interviews. The key capabilities elicited from our survey of business users in this section include: decentralization, multi-cloud deployment, elastic scaling on-demand, fault tolerance and high availability, access control and data governance. Any successful solution needs to exhibit these characteristics if it’s going to meet business user demands.
Benchmarking
From a quantitative perspective, we benchmarked two popular permissioned blockchains, Fabric and Quorum, against our serverless implementation in terms of throughput and costs.
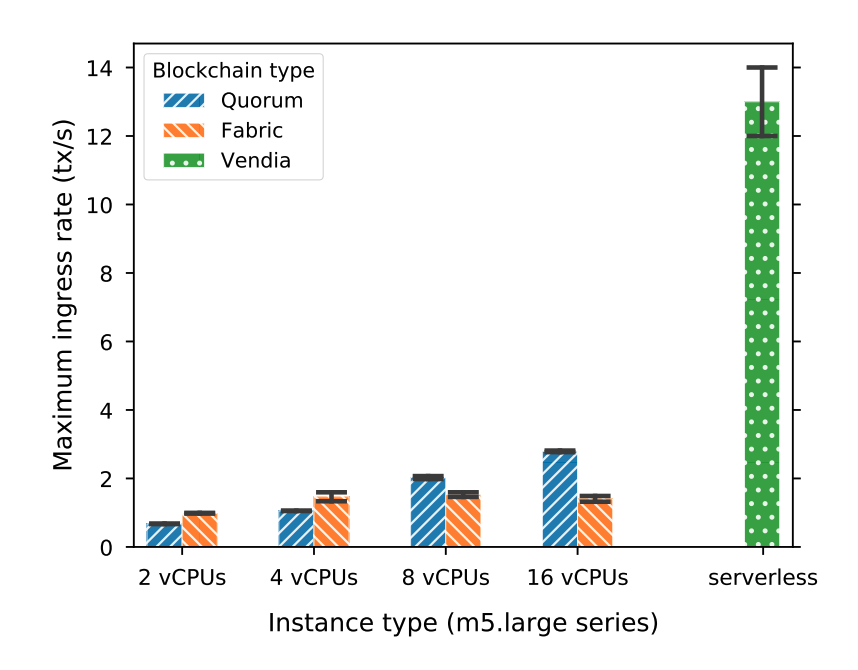
Our research indicates that our current implementation already improves on multiple performance aspects – including transaction ingress rates well in excess of those achievable through conventional means, while further optimizations promise to outperform existing permissioned blockchains through readily exploited avenues, such as decoupling of transaction content copying from consensus.
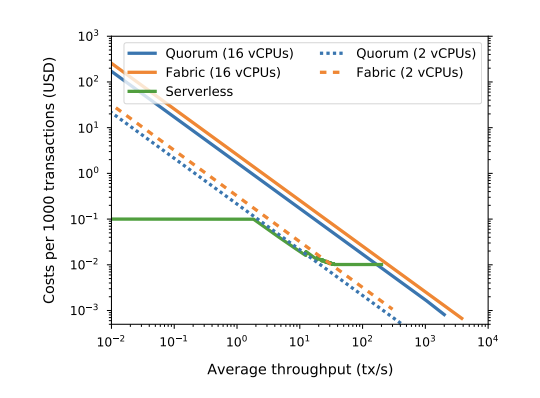
Here are a couple figures: one that shows maximum ingress rates for different intercontinental network configurations, and the following that compares per-transaction costs for Fabric, Quorum and our serverless solution depending on average throughput, illustrating that we can also lower the costs of transactions (even for private, permissioned networks) dramatically … while costs versus public networks such as Ethereum are many orders of magnitude lower.
Get the Paper
Check out the full research paper here on arXiv for more detail, including our plan for future research, references, and more.